
–by Dr. Peng E. Wang
Introduction
Vitamin D is an essential vitamin that humans need to function optimally, in addition to the absorption of calcium it’s also linked to other diseases. Due to external and internal factors, most of us are deficient in vitamin D (NCBI). We commonly associate vitamin D with bone density, risk of hip fracture, and Ricketts, but it’s more than that. Vitamin D is an important factor in autoimmune disorders such as Multiple Sclerosis, and in mental health, as well as musculoskeletal diseases. In contrast, excessive vitamin D supplementation without monitoring can be fatal (NCBI). So how do you check for vitamin D? How do you supplement and monitor it appropriately? Let’s take a look at the appropriate management of this common deficiency.
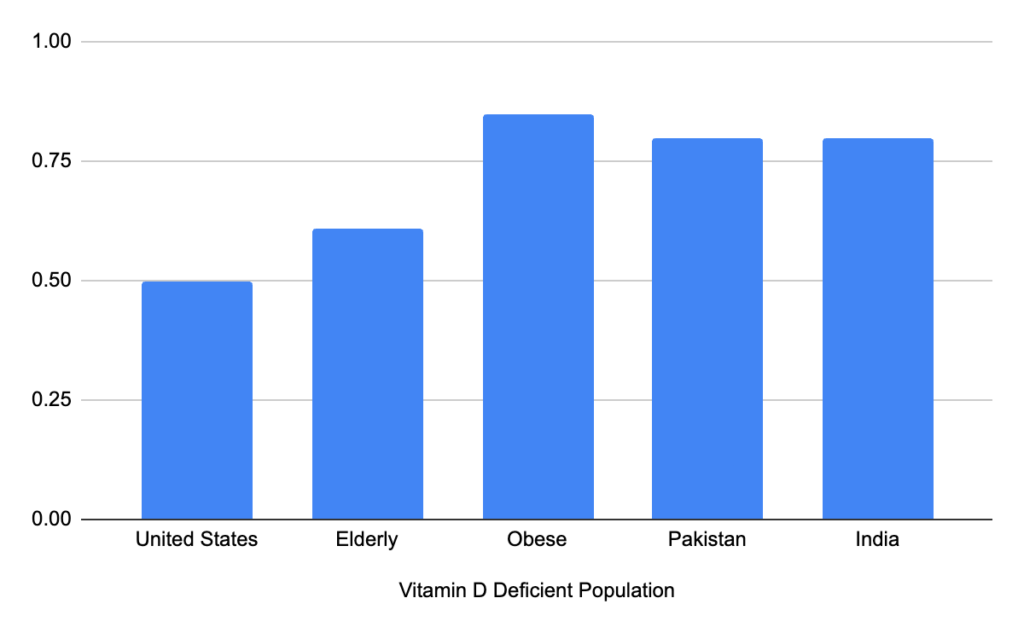
Overview
Why is my vitamin D level low? Should I take vitamin D or D3? How long do you need to be in the sun for vitamin D? Should I even worry about vitamin D? What are the symptoms of low vitamin D? All valid questions we will try to answer, but the short answer is yes, you should be worried about your vitamin D levels.
Humans are commonly low in this essential vitamin because we wear clothing, get sheltered from the Sun, live in cold climates, eat processed foods, take synthetic medications (i.e. Omeprazole) for certain diseases, are biologically different, and have unequal access to proper nutrition. This list is not comprehensive but covers the most common risk factors (NCBI).
Symptoms of vitamin D deficiency may be very vague and subtle, you should know what they may be in different contexts. The symptoms typically do not occur overnight, and you may not be correlating it with a low vitamin D level. This emphasizes the importance of checking your vitamin D level annually.
The treatment for vitamin D may seem simple by just finding a supplement and start taking it, but there are many factors to consider when treating vitamin D deficiency.
Symptoms of low vitamin D
- A child is walking late
- The child walking appears to be bowed in the legs
- Adults with chronic muscle aches and pains (>90 days)
- Adults with sternum pain when pressed
- Adults with tibia pain when pressed
- Fatigue and tiredness
- Slow wound healing
- Muscle weakness
- Frequent falls
- Dental issues
- Depression
- Seizures
Symptoms of vitamin toxicity (excessive)
- Nausea and vomiting
- Other unclear gastrointestinal symptoms
- Abdominal pain around your pancreas region
- Metallic taste
- Headaches
Risk factors
- Obesity (reduced availability, sequestration)
- Dark skin (synthesis stifled)
- Over 65 years old (thinner skin, less storage)
- Infants that are breastfed (less in breast milk)
- Chronic kidney disease (less conversion to active D)
- Chronic liver disease (storage is less)
- Absorption issues such as Celiac disease
- Weight loss surgery-induced absorption issues
- Medications reduce absorption (i.e. Omeprazole)
Complications of vitamin D deficiency
| Vitamin D level (ng/mL) | % of participants in the study | # of participants in the study |
| >30 | 4.8% | 35 |
| 20-29 | 11.9% | 87 |
| 10-19 | 36.1% | 264 |
| <10 | 47.3% | 346 |
This table demonstrates the higher risk of hip fracture with lower vitamin D levels, notice the inverse relationship. While having a normal vitamin D level does not eliminate the risk of hip fracture, it’s 10 times less than elderly with <10 ng/mL of 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels.
*Low energy means just stepping off a curb or taking a misstep on stairs and stumbling; low impacts of normal daily routines. Based on clinical criteria, if you fall from a height less than your own (fall forward), you should not have broken your hip, otherwise suspect osteoporosis (NIH).
Vitamin D Testing
- A blood test ordered by a healthcare provider
- You can also request testing at multiple online resources including LabCorp or Quest
- Not affected by how much vitamin D you are taking now
- The standard test is 25-hydroxyvitamin or 25(OH)D, or ergocalciferol
- It’s not a fasting lab (you can eat)
| Normal | 50-75 nmol/L |
| Deficient | 25-50 nmol/L |
| Severely deficient | <25 nmol/L |
| Optimal | 75-100 nmol/L |
| Excessive | >150 nmol/L |
When should you test for the vitamin D level? When you suspect any symptoms may be related to vitamin D deficiency, or during an annual wellness checkup particularly if you have the risks.
Treatments for vitamin D deficiency
- Drisdol, the active ingredient is ergocalciferol (vitamin D2)
- Cholecalciferol, the active ingredient is 1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol (vitamin D3)
Should you take vitamin D2 or D3? Overall, vitamin D3 is preferred over D2 due to better support for your immune system, although D2 may increase your 25(OH)D level faster due to a higher dosing regimen, it does not necessarily mean a better health response. Vitamin D3 supplementation has demonstrated an improved immune system while D2 did not (Medscape).
This is likely due to the hormonal effect of vitamin D3 improving other system functions, including cell response and immunity since D3 is activated (NIH). 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D, or D3, is active D and is currently being compared as a hormone. Vitamin D is not just a vitamin, another reason it’s important to check its level more than other vitamins.
How long does it take to increase your vitamin D level? Typically 2-4 weeks, but keep in mind that’s the 25(OH)D level checked in the bloodstream, this does not mean it’s providing you any benefit since only D3 is active.
Conclusion:
Vitamin D deficiency contributes to serious health risks, particularly in the elderly population who are at risk for falls and hip fractures caused by osteoporosis. It’s important to address this issue considering that most of us are deficient due to lifestyles, location, diet, and many other factors. Also treating vitamin D deficiency takes time, it does not happen overnight, and it’s best to be monitored regularly with blood testing. Vitamin D3 surpasses the benefits of vitamin D2, due to its other prohormonal effects on other systems and faster activation.
Bonus: Vitamin D Absorption and Activation
How is vitamin D absorbed? Typically through your diet (AAFP). Vitamin D gets stored in the skin and needs ultraviolet radiation (UV) to start the activation process, thus Sunlight activates it instead of “giving” it. The next steps involve the liver and kidney before it’s active, which is hydroxylation (-OH). Why is this important to know? The Sunlight you get during the summertime starts the process of Vitamin D activation, and by the time it gets hydroxylated in your liver and kidney before it’s active six months have passed. You guessed right, your vitamin D level is highest in the Winter. The moral of the lesson is do not chase your vitamin D level too harshly as there are factors out of your control. If you take vitamin D consistently while the level is increasing, albeit slowly, but you are feeling better, that’s what matters. However, does vitamin D3 need Sunlight since it’s active? Let me know in the comments.
Related article: COVID-19 Symptoms and Treatments