
–by Dr. Peng E. Wang
Introduction
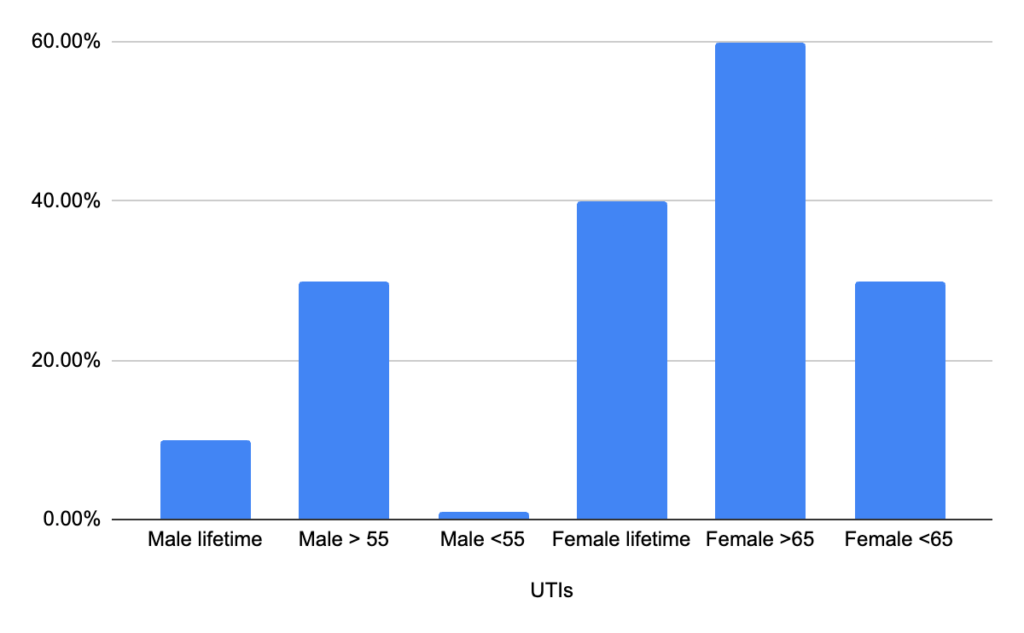
Urinary symptoms are one of the most common reasons for a consumer to seek healthcare. When combining clinic visits (~10 million) and ER visits (2-3 million), urinary issues cost more than 3 billion USD due to care spending and loss in productivity (NIH). Urinary issues based on age and associated symptoms should be evaluated and managed promptly to avoid complications. Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are not always independent, meaning other associated health issues are commonly involved, such as Benign Prostatic Hypertrophy (BPH) in males and incontinence issues in females. UTI is a constellation of symptoms; understanding the underlying reasons optimizes its management and prevention. Let’s look at the symptoms, differentials, management, complications, and self-care options of UTIs.
Overview
The constellation of UTI symptoms typically includes burning urination, frequency and urgency of urination, and changes in urine, with or without fever or back pains (Wiki). However, it’s more important to determine the underlying reason and what you can do to avoid it next time.
Aside from UTI other causes of urinary symptoms include kidney stones, enlarged prostate, incontinence, yeast infection, Sexually Transmitted Disease (STD), and overactive bladder. A few questions can help to determine the cause.
- Urinary symptoms involve a discharge? Likely vaginitis.
- Sudden onset of flank pain (upper back)? Likely kidney stones.
- Coughing, laughing, and lifting cause urine leakage—likely incontinence.
- Male age <45 years old with urinary symptoms, likely urethritis. Needs testing.
- Male age >45 years old with urinary symptoms, likely enlarged prostate, get testing.
- Female age >50 with recurrent UTI symptoms and incontinence. Weak pelvic floor muscles.
- Blood in urine but no other symptoms? Please seek urological care.
Context is crucial while working up urinary symptoms because it helps to isolate a urinary issue from other causes. By deduction, you can get clues of what the urinary issue is caused by; not every case of urinary symptoms is due to a UTI.
Common questions asked by consumers
- What are the most common 3 symptoms of a UTI?
- Does UTI go away on its own?
- Is it a UTI or a yeast infection?
- Is it a UTI or my period?
- Is it a UTI or STD?
UTI Symptoms
Common
- Urinary urgency
- Frequent urination
- Burning while urinating
- Incomplete emptying of urine
- Cloudy urine with a stronger smell
- The feeling of not completely emptying
- Feverish feeling with temp <100°Fahrenheit (37.8°Celsius)
Less common
- Fever above 100.4 °Fahrenheit (38 °Celsius)
- Flank pains (upper back)
- Blood in urine
- Urine leakage
- Nausea
Uncommon
- Severe abdominal pain (other underlying health conditions)
- Wax and wean of urinary symptoms prolonged
- Blood clots that are stringy in urine (hemorrhagic cystitis)
- Bladder spasms (neurogenic bladder)
Other referred
- Vaginal itching and thick discharge (yeast infection)
- Vaginal burning with thin discharge and odor (bacterial vaginosis or BV)
- Suprapubic pains (above groin) due to menstruation cycle, vaginal bleeding (hematuria)
- Urinary frequency, nighttime wakenings in males without burning/pain, enlarged prostate
- Urine leakage with coughing, laughing, lifting in females, incontinence, weak pelvic floor
- Urinary frequency and nighttime wakenings in females, urinary retention likely
- Urinary urgency with incontinence, consider OAB (overactive bladder)
Urinary Symptoms Treatments
Self-care tips
- Stay hydrated with an adequate amount of water intake daily
- Practice good urinary habits by practicing bladder training methods
- Limit caffeine and alcohol intake particularly when it’s toward the evening
- Kegel exercises for known incontinence issues
- Voiding before and after sexual activity
- Biofeedback and bladder training for OAB (overactive bladder)
Anti–spasmodic (Over-The-Counter or prescribed)
- AZO Standard, the active ingredient is phenazopyridine, use it <48 hours
- Pyridium, the active ingredient is phenazopyridine, use it <48 hours continuously
Antibiotics (prescription only)
- Macrobid, the active ingredient is nitrofurantoin, the most effective 1st line therapy
- Macrodantin, the active ingredient is nitrofurantoin, effective, and has less resistance
- Bactrim, the active ingredients are sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim, 2nd choice
- Septra, the active ingredients are sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim
- Keflex, the active ingredient is cephalexin, a sound choice for pregnancy
- Amoxil, the active ingredient is amoxicillin, a sound choice for pregnancy
- Cipro, the active ingredient is ciprofloxacin, a short course of 3 days, (Not 1st choice)
Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) (prescription only)
- Estrogen is effective for menopause treatment which can cause UTIs
- Progesterone opposes estrogen estrogen HRT to prevent cancer of the uterus
Incontinence and Overactive Bladder treatments (prescriptions only)
- Elavil, the active ingredient is amitriptyline, an anti-spasm
- Detrol, the active ingredient is tolterodine, a bladder relaxer
- Vesicare, the active ingredient is solifenacin
- Ditropan, the active ingredient is oxybutynin, a bladder relaxer and antispasmodic
- Sanctura, the active ingredient is trospium, both relaxer and antispasmodic
- Myrbetriq, the active ingredient is mirabegron, a relaxer using a beta-blocking effect
- Botox, the active ingredient is botulinum, a neurotoxin that relaxes the bladder muscles
Prostate induced urinary issues (prescription)
- Flomax, the active ingredient is tamsulosin
- Avodart, the active ingredient is dutasteride
- Proscar, the active ingredient is finasteride
- Hytrin, the active ingredient is terazosin
Supplemental preventive (Over-the-counter)
- Cranberry, chose capsules over juice (less sugar), up to 20% reduction of UTI recurrence (NIH)
- Probiotics, specifically Lactobacillus rhamnosus is the most effective (NCBI)
- D-Mannose binds microorganisms to flush them out
- Potassium citrate alkalizes the urine and unlocks the power of D-Mannose
- Citric acid alkalizes the urine as well
- Vitamin C improves immunity
- Vitamin D3 improves bladder wall integrity
- Vitamin B6, gentle diuretic
Complications and Prevention
Physical defense system
Aside from the body’s natural chemistry to keep the bladder sterile, anatomical barriers prevent excessive amounts of microbes from invading the bladder. The importance of pelvic floor muscle integrity should be emphasized because it’s an additional gate to the sphincter (muscle) at the bladder-urethra junction (#6) on this diagram. Many events challenge this junction, including not emptying the bladder on time, intercourse, menstruation, coughing, swimming, and many more. Any pressure changes that cause the reflux of urine from the urethra into the bladder can induce UTI symptoms.
Risk factors for UTIs
- Previous history of UTI
Complications (Urgent care or emergency room)
- Fever >100.4F with upper back pain and nausea (Pyelonephritis)
- Gross hematuria (visible blood) with lightheadedness, dizziness
- Severe abdominal pain suggests other underlying abdominal process
When to see a doctor in the office
- Recurring UTIs, >3 in 12 months
- Recurring yeast infections or BV symptoms
- Changes in urine without symptoms such as burning
- Urinary symptoms unexplained and ongoing (>2 weeks)
Prevention
- Stay hydrated with an adequate amount of water intake daily
- Practice good urinary habits by practicing bladder training methods
- Limit caffeine and alcohol intake particularly when it’s toward the evening
- Kegel exercises for known incontinence issues
- Voiding before and after sexual activity
Conclusion
While it’s not possible to cover all causes of urinary symptoms in this article, there are common causes and patterns we can recognize to determine the best way to manage them. In general, UTI occurs in females mostly, and males over the age of 50 with prostate issues, otherwise UTIs should be a rare occurrence. The constellation of UTI symptoms is a warning sign indicating there is an issue in the functional system. By reviewing the treatments of UTIs above they include other conditions such as prostate issues, menopause issues, and neurogenic bladder. The takeaway is that urinary symptoms should prompt you to think of an underlying health issue, especially when it’s recurring or without any obvious reasoning. Recognizing the pattern of different diseases helps to guide us to sound management.
Bonus: Urinary VS. Respiratory Infections in Context
Many health conditions put you at risk for urinary issues, but when compared to respiratory infections, it’s less common. The main reason is exposure. The air you breathe is heavily concentrated with pathogens, including mold, dust mites, viruses, and many other unidentified microbes (NCBI). While it’s difficult to determine the respiratory pathogens that cause the cold, when it comes to a UTI, they are mostly bacterial. Respiratory symptoms are commonly self-managed initially without the need for prescription medications, but the onset of urinary symptoms should be managed timely with a medical professional considering it’s less common and more urgent.

Related article: 7 Common Medications for Cough